Accept in-app payments
Build a customized payments integration in your iOS, Android, or React Native app using the Payment Sheet.
The Payment Sheet is a customizable component that displays a list of payment methods and collects payment details in your app using a bottom sheet.
Compare Customers v1 and Accounts v2 references
If your Connect platform uses customer-configured Accounts, use our guide to replace Customer and event references in your code with the equivalent Accounts v2 API references.
A SetupIntent flow allows you to collect payment method details and save them for future payments without creating a charge. In this integration, you build a custom flow where you render the Payment Element, create the SetupIntent, and confirm saving the payment method in your app.
Set up StripeServer-sideClient-side
First, you need a Stripe account. Register now.
Server-side
This integration requires endpoints on your server that talk to the Stripe API. Use the official libraries for access to the Stripe API from your server:
Client-side
The Stripe Android SDK is open source and fully documented.
To install the SDK, add stripe-android to the dependencies block of your app/build.gradle file:
Note
For details on the latest SDK release and past versions, see the Releases page on GitHub. To receive notifications when a new release is published, watch releases for the repository.
You also need to set your publishable key so that the SDK can make API calls to Stripe. To get started quickly, you can hardcode this on the client while you’re integrating, but fetch the publishable key from your server in production.
// Set your publishable key: remember to change this to your live publishable key in production // See your keys here: https://dashboard.stripe.com/apikeys PaymentConfiguration.init(context, publishableKey =)"pk_test_TYooMQauvdEDq54NiTphI7jx"
Enable payment methods
View your payment methods settings and enable the payment methods you want to support. You need at least one payment method enabled to create a SetupIntent.
By default, Stripe enables cards and other prevalent payment methods that can help you reach more customers, but we recommend turning on additional payment methods that are relevant for your business and customers. See Payment method support for product and payment method support, and our pricing page for fees.
Create a CustomerServer-side
To set up a payment method for future payments, you must attach it to a Customer. Create a Customer object when your customer creates an account with your business. Customer objects allow for reusing payment methods and tracking across multiple payments.
Compare Customers v1 and Accounts v2 references
If your Connect platform uses customer-configured Accounts, use our guide to replace Customer and event references in your code with the equivalent Accounts v2 API references.
Collect payment detailsClient-side
We offer two styles of integration.
| PaymentSheet | PaymentSheet.FlowController |
|---|---|
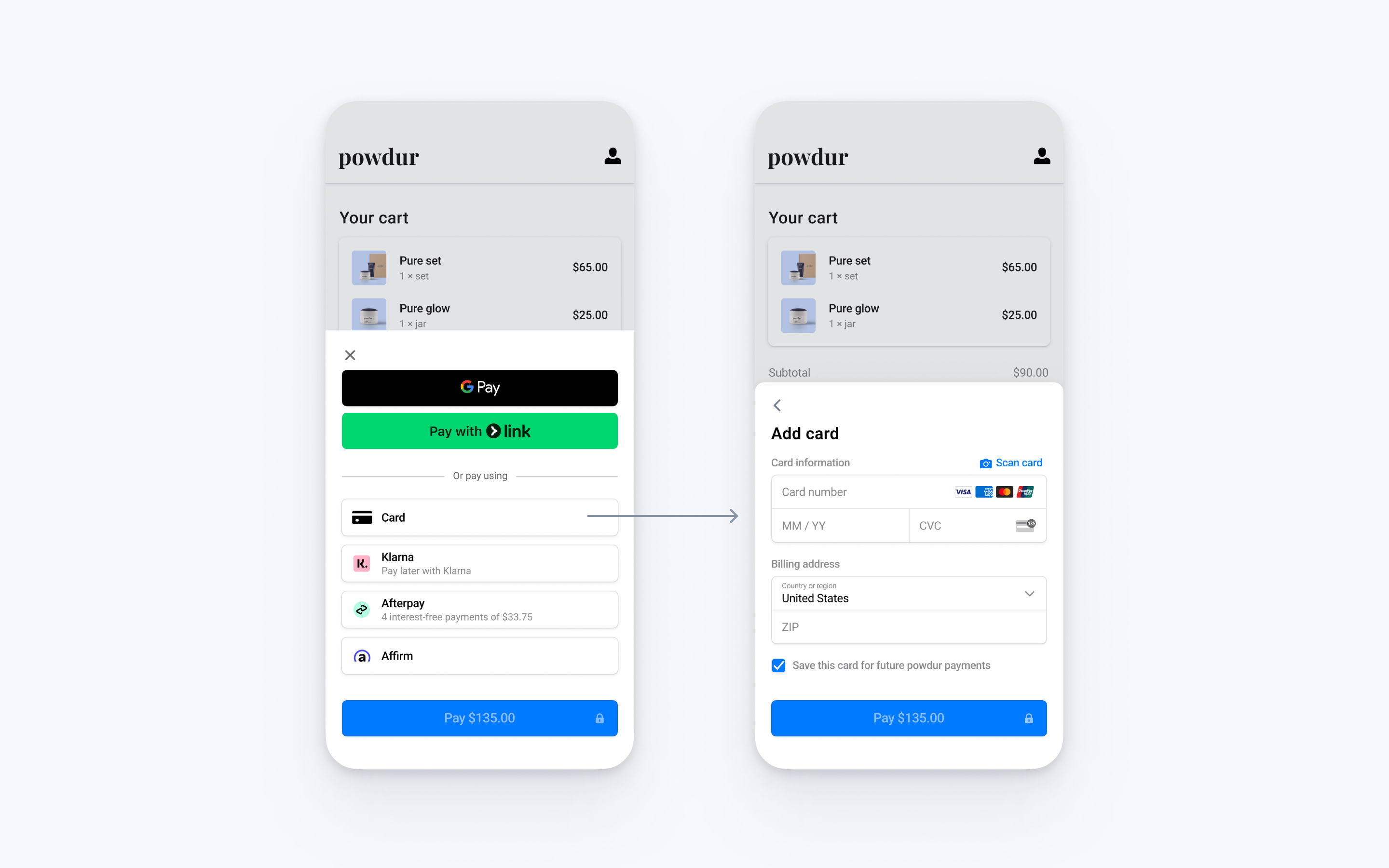 |  |
| Displays a sheet to collect and save payment details. The button label is Set up. Clicking it saves the payment details. | Displays a sheet to only collect payment details. The button label is Continue. Clicking it returns the customer to your app, where your own button saves the payment details. |
Create a SetupIntentServer-side
On your server, create a SetupIntent. You can manage payment methods from the Dashboard. Stripe evaluates payment method restrictions and other parameters to determine the list of supported payment methods.
If the call succeeds, return the SetupIntent client secret. If the call fails, handle the error and return an error message with a brief explanation for your customer.
Note
Verify that all IntentConfiguration properties match your SetupIntent (for example, usage).
Charge the saved payment method laterServer-side
Warning
bancontact and ideal are one-time payment methods by default. When set up for future usage, they generate a sepa_ reusable payment method type so you need to use sepa_ to query for saved payment methods.
Compliance
You’re responsible for your compliance with all applicable laws, regulations, and network rules when saving a customer’s payment details. When rendering past payment methods to your end customer for future purchases, make sure you’re listing payment methods where you’ve collected consent from the customer to save the payment method details for this specific future use. To differentiate between payment methods attached to customers that can and can’t be presented to your end customer as a saved payment method for future purchases, use the allow_redisplay parameter.
When you’re ready to charge your customer off-session, use the Customer and PaymentMethod IDs to create a PaymentIntent. To find a payment method to charge, list the payment methods associated with your customer. This example lists cards but you can list any supported type.
When you have the Customer and PaymentMethod IDs, create a PaymentIntent with the amount and currency of the payment. Set a few other parameters to make the off-session payment:
- Set off_session to
trueto indicate that the customer isn’t in your checkout flow during a payment attempt and can’t fulfill an authentication request made by a partner, such as a card issuer, bank, or other payment institution. If, during your checkout flow, a partner requests authentication, Stripe requests exemptions using customer information from a previous on-session transaction. If the conditions for exemption aren’t met, the PaymentIntent might throw an error. - Set the value of the PaymentIntent’s confirm property to
true, which causes confirmation to occur immediately when the PaymentIntent is created. - Set payment_method to the ID of the PaymentMethod and customer to the ID of the Customer.
Test the integration
See Testing for additional information to test your integration.
OptionalEnable saved cardsServer-sideClient-side
PaymentSheet can allow the customer to save their card and can include the customer’s saved cards in available payment methods. The customer must have an associated Customer object on your server. To enable a checkbox that allows the customer to save their card, create a CustomerSession, with payment_ set to enabled.
const stripe = require("stripe")(); const express = require('express'); const app = express(); app.set('trust proxy', true); app.use(express.json()); app.post('/payment-sheet', async (req, res) => { // Use an existing Customer ID if this is a returning customer. const customer = await stripe.customers.create(); const customerSession = await stripe.customerSessions.create({ customer: customer.id, components: { mobile_payment_element: { enabled: true, features: { payment_method_save: 'enabled', payment_method_redisplay: 'enabled', payment_method_remove: 'enabled' } }, }, }); res.json({ customerSessionClientSecret: customerSession.client_secret, customer: customer.id, }); });"sk_test_BQokikJOvBiI2HlWgH4olfQ2"
Next, present PaymentSheet with the Customer’s ID and the CustomerSession client secret.
val configuration = PaymentSheet.Configuration.Builder(merchantDisplayName = "Powdur") .customer( PaymentSheet.CustomerConfiguration.createWithCustomerSession( id = customerId, clientSecret = customerSessionClientSecret, ) ) .build() paymentSheet.presentWithIntentConfiguration( intentConfiguration = // ... , configuration = configuration, )
OptionalAllow delayed payment methodsClient-side
Delayed payment methods don’t guarantee that you’ll receive funds from your customer at the end of checkout, either because they take time to settle (for example, US Bank Accounts, SEPA Debit, iDEAL, Bancontact, and Sofort) or because they require customer action to complete (for example, OXXO, Konbini, and Boleto).
By default, PaymentSheet doesn’t display delayed payment methods. To include the delayed payment methods that PaymentSheet supports, set allowsDelayedPaymentMethods to true in your PaymentSheet..
val configuration = PaymentSheet.Configuration.Builder(merchantDisplayName = "Powdur") .allowsDelayedPaymentMethods(true) .build()
If the customer successfully uses a delayed payment method in a PaymentSheet, the payment result returned is PaymentSheetResult..
OptionalEnable Google Pay
Note
If your checkout screen has a dedicated Google Pay button, follow the Google Pay guide. You can use Embedded Payment Element to handle other payment method types.
Set up your integration
To use Google Pay, first enable the Google Pay API by adding the following to the <application> tag of your AndroidManifest.xml:
<application> ... <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.wallet.api.enabled" android:value="true" /> </application>
For more details, see Google Pay’s Set up Google Pay API for Android.
Add Google Pay
To add Google Pay to your integration, pass a PaymentSheet.GooglePayConfiguration with your Google Pay environment (production or test) and the country code of your business when initializing PaymentSheet.Configuration.
Test Google Pay
Google allows you to make test payments through their Test card suite. The test suite supports using Stripe test cards.
You must test Google Pay using a physical Android device instead of a simulated device, in a country where Google Pay is supported. Log in to a Google account on your test device with a real card saved to Google Wallet.
OptionalEnable card scanning
To enable card scanning support, request production access to the Google Pay API from the Google Pay and Wallet Console.
- If you’ve enabled Google Pay, the card scanning feature is automatically available in our UI on eligible devices. To learn more about eligible devices, see the Google Pay API constraints
- Important: The card scanning feature only appears in builds signed with the same signing key registered in the Google Pay & Wallet Console. Test or debug builds using different signing keys (for example, builds distributed through Firebase App Tester) won’t show the Scan card option. To test card scanning in pre-release builds, you must either:
- Sign your test builds with your production signing key
- Add your test signing key fingerprint to the Google Pay and Wallet Console
OptionalCustomize the sheet
All customization is configured using the PaymentSheet.Configuration object.
Appearance
Customize colors, fonts, and more to match the look and feel of your app by using the appearance API.
Payment method layout
Configure the layout of payment methods in the sheet using paymentMethodLayout. You can display them horizontally, vertically, or let Stripe optimize the layout automatically.

Collect users addresses
Collect local and international shipping or billing addresses from your customers using the Address Element.
Business display name
Specify a customer-facing business name by setting merchantDisplayName. By default, this is your app’s name.
Dark mode
By default, PaymentSheet automatically adapts to the user’s system-wide appearance settings (light and dark mode). You can change this by setting light or dark mode on your app:
Default billing details
To set default values for billing details collected in the payment sheet, configure the defaultBillingDetails property. The PaymentSheet pre-populates its fields with the values that you provide.
Configure collection of billing details
Use BillingDetailsCollectionConfiguration to specify how you want to collect billing details in the PaymentSheet.
You can collect your customer’s name, email, phone number, and address.
If you want to attach default billing details to the PaymentMethod object even when those fields aren’t collected in the UI, set billingDetailsCollectionConfiguration. to true.
Note
Consult with your legal counsel regarding laws that apply to collecting information. Only collect phone numbers if you need them for the transaction.