Accept a payment
Securely accept payments online.
Build a payment form or use a prebuilt checkout page to start accepting online payments.
Not a developer?
Use Stripe’s no-code options or apps from our partners to get started and do more with your Stripe account—no code required. If you use a third-party platform to build and maintain a website, you can add Stripe payments with a plugin.
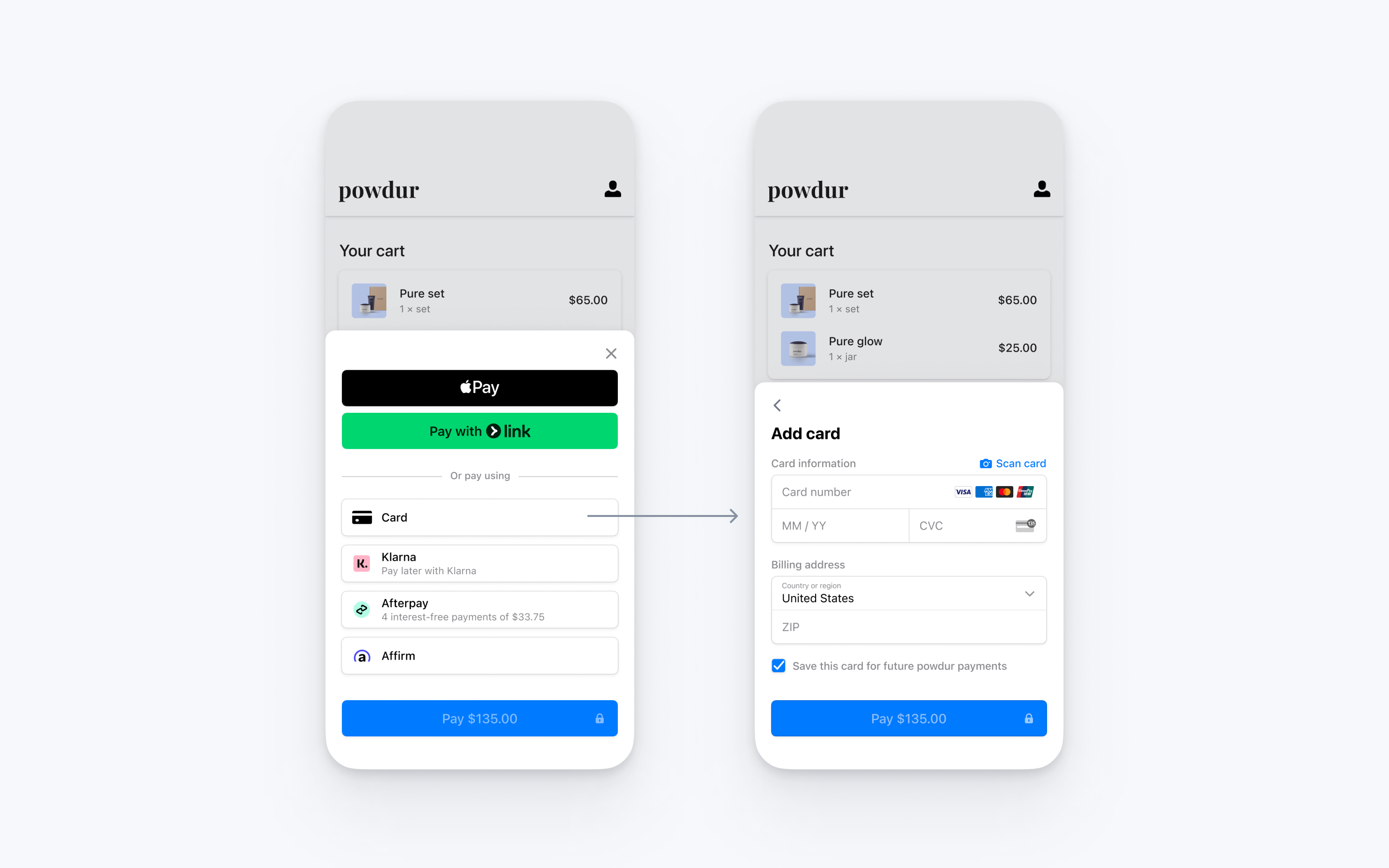
This integration combines all of the steps required to pay, including collecting payment details and confirming the payment, into a single sheet that displays on top of your app.
Set up StripeServer-sideClient-side
First, you need a Stripe account. Register now.
Server-side
This integration requires endpoints on your server that talk to the Stripe API. Use the official libraries for access to the Stripe API from your server:
Client-side
The React Native SDK is open source and fully documented. Internally, it uses the native iOS and Android SDKs. To install Stripe’s React Native SDK, run one of the following commands in your project’s directory (depending on which package manager you use):
Next, install some other necessary dependencies:
- For iOS, go to the ios directory and run
pod installto ensure that you also install the required native dependencies. - For Android, there are no more dependencies to install.
Note
We recommend following the official TypeScript guide to add TypeScript support.
Stripe initialisation
To initialise Stripe in your React Native app, either wrap your payment screen with the StripeProvider component, or use the initStripe initialisation method. Only the API publishable key in publishableKey is required. The following example shows how to initialise Stripe using the StripeProvider component.
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react'; import { StripeProvider } from '@stripe/stripe-react-native'; function App() { const [publishableKey, setPublishableKey] = useState(''); const fetchPublishableKey = async () => { const key = await fetchKey(); // fetch key from your server here setPublishableKey(key); }; useEffect(() => { fetchPublishableKey(); }, []); return ( <StripeProvider publishableKey={publishableKey} merchantIdentifier="merchant.identifier" // required for Apple Pay urlScheme="your-url-scheme" // required for 3D Secure and bank redirects > {/* Your app code here */} </StripeProvider> ); }
Enable payment methods
View your payment methods settings and enable the payment methods you want to support. You need at least one payment method enabled to create a PaymentIntent.
By default, Stripe enables cards and other prevalent payment methods that can help you reach more customers, but we recommend turning on additional payment methods that are relevant for your business and customers. See Payment method support for product and payment method support, and our pricing page for fees.
Add an endpointServer-side
Note
To display the PaymentSheet before you create a PaymentIntent, see Collect payment details before creating an Intent.
This integration uses three Stripe API objects:
PaymentIntent: Stripe uses this to represent your intent to collect payment from a customer, tracking your charge attempts and payment state changes throughout the process.
(Optional) Customer: To set up a payment method for future payments, you must attach it to a Customer. Create a Customer object when your customer creates an account with your business. If your customer is making a payment as a guest, you can create a Customer object before payment and associate it with your own internal representation of the customer’s account later.
(Optional) CustomerSession: Information on the Customer object is sensitive, and can’t be retrieved directly from an app. A CustomerSession grants the SDK temporary scoped access to the Customer and provides additional configuration options. See a complete list of configuration options.
Note
If you never save cards to a Customer and don’t allow returning Customers to re-use saved cards, you can omit the Customer and CustomerSession objects from your integration.
For security reasons, your app can’t create these objects. Instead, add an endpoint on your server that:
- Retrieves the Customer, or creates a new one.
- Creates a CustomerSession for the Customer.
- Creates a PaymentIntent with the amount, currency, and customer.
- Returns the Payment Intent’s client secret, the CustomerSession’s
client_, the Customer’s id, and your publishable key to your app.secret
The payment methods shown to customers during the checkout process are also included on the PaymentIntent. You can let Stripe pull payment methods from your Dashboard settings or you can list them manually. Regardless of the option you choose, note that the currency passed in the PaymentIntent filters the payment methods shown to the customer. For example, if you pass eur on the PaymentIntent and have OXXO enabled in the Dashboard, OXXO won’t be shown to the customer because OXXO doesn’t support eur payments.
Unless your integration requires a code-based option for offering payment methods, Stripe recommends the automated option. This is because Stripe evaluates the currency, payment method restrictions, and other parameters to determine the list of supported payment methods. Payment methods that increase conversion and that are most relevant to the currency and customer’s location are prioritised.
Collect payment detailsClient-side
Before displaying the mobile Payment Element, your checkout page should:
- Show the products being purchased and the total amount
- Collect any required shipping information
- Include a checkout button to present Stripe’s UI
In the checkout of your app, make a network request to the backend endpoint you created in the previous step and call initPaymentSheet from the useStripe hook.
export default function CheckoutScreen() { const { initPaymentSheet, presentPaymentSheet } = useStripe(); const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false); const fetchPaymentSheetParams = async () => { const response = await fetch(`${API_URL}/payment-sheet`, { method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', }, }); const { paymentIntent, ephemeralKey, customer } = await response.json(); return { paymentIntent, ephemeralKey, customer, }; }; const initializePaymentSheet = async () => { const { paymentIntent, ephemeralKey, customer, } = await fetchPaymentSheetParams(); const { error } = await initPaymentSheet({ merchantDisplayName: "Example, Inc.", customerId: customer, customerEphemeralKeySecret: ephemeralKey, paymentIntentClientSecret: paymentIntent, // Set `allowsDelayedPaymentMethods` to true if your business can handle payment //methods that complete payment after a delay, like SEPA Debit and Sofort. allowsDelayedPaymentMethods: true, defaultBillingDetails: { name: 'Jane Doe', } }); if (!error) { setLoading(true); } }; const openPaymentSheet = async () => { // see below }; useEffect(() => { initializePaymentSheet(); }, []); return ( <Screen> <Button variant="primary" disabled={!loading} title="Checkout" onPress={openPaymentSheet} /> </Screen> ); }
When your customer taps the Checkout button, call presentPaymentSheet() to open the sheet. After the customer completes the payment, the sheet is dismissed and the promise resolves with an optional StripeError<PaymentSheetError>.
export default function CheckoutScreen() { // continued from above const openPaymentSheet = async () => { const { error } = await presentPaymentSheet(); if (error) { Alert.alert(`Error code: ${error.code}`, error.message); } else { Alert.alert('Success', 'Your order is confirmed!'); } }; return ( <Screen> <Button variant="primary" disabled={!loading} title="Checkout" onPress={openPaymentSheet} /> </Screen> ); }
If there is no error, inform the user they’re done (for example, by displaying an order confirmation screen).
Setting allowsDelayedPaymentMethods to true allows delayed notification payment methods like US bank accounts. For these payment methods, the final payment status isn’t known when the PaymentSheet completes, and instead succeeds or fails later. If you support these types of payment methods, inform the customer their order is confirmed and only fulfil their order (for example, ship their product) when the payment is successful.
Set up a return URL (iOS only)Client-side
When a customer exits your app (for example to authenticate in Safari or their banking app), provide a way for them to automatically return to your app. Many payment method types require a return URL. If you don’t provide one, we can’t present payment methods that require a return URL to your users, even if you’ve enabled them.
To provide a return URL:
- Register a custom URL. Universal links aren’t supported.
- Configure your custom URL.
- Set up your root component to forward the URL to the Stripe SDK as shown below.
Note
If you’re using Expo, set your scheme in the app. file.
import { useEffect, useCallback } from 'react'; import { Linking } from 'react-native'; import { useStripe } from '@stripe/stripe-react-native'; export default function MyApp() { const { handleURLCallback } = useStripe(); const handleDeepLink = useCallback( async (url: string | null) => { if (url) { const stripeHandled = await handleURLCallback(url); if (stripeHandled) { // This was a Stripe URL - you can return or add extra handling here as you see fit } else { // This was NOT a Stripe URL – handle as you normally would } } }, [handleURLCallback] ); useEffect(() => { const getUrlAsync = async () => { const initialUrl = await Linking.getInitialURL(); handleDeepLink(initialUrl); }; getUrlAsync(); const deepLinkListener = Linking.addEventListener( 'url', (event: { url: string }) => { handleDeepLink(event.url); } ); return () => deepLinkListener.remove(); }, [handleDeepLink]); return ( <View> <AwesomeAppComponent /> </View> ); }
Additionally, set the returnURL when you call the initPaymentSheet method:
await initPaymentSheet({ ... returnURL: 'your-app://stripe-redirect', ... });
For more information on native URL schemes, refer to the Android and iOS docs.
Handle post-payment events
Stripe sends a payment_intent.succeeded event when the payment completes. Use the Dashboard webhook tool or follow the webhook guide to receive these events and run actions, such as sending an order confirmation email to your customer, logging the sale in a database, or starting a shipping workflow.
Listen for these events rather than waiting on a callback from the client. On the client, the customer could close the browser window or quit the app before the callback executes, and malicious clients could manipulate the response. Setting up your integration to listen for asynchronous events is what enables you to accept different types of payment methods with a single integration.
In addition to handling the payment_ event, we recommend handling these other events when collecting payments with the Payment Element:
| Event | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| payment_intent.succeeded | Sent when a customer successfully completes a payment. | Send the customer an order confirmation and fulfill their order. |
| payment_intent.processing | Sent when a customer successfully initiates a payment, but the payment has yet to complete. This event is most commonly sent when the customer initiates a bank debit. It’s followed by either a payment_ or payment_ event in the future. | Send the customer an order confirmation that indicates their payment is pending. For digital goods, you might want to fulfill the order before waiting for payment to complete. |
| payment_intent.payment_failed | Sent when a customer attempts a payment, but the payment fails. | If a payment transitions from processing to payment_, offer the customer another attempt to pay. |
Test the integration
See Testing for additional information to test your integration.
Enable card scanningClient-side
Note
Enabling card scanning is required for Apple’s iOS app review process. Card scanning is not required for Android’s app review process, but we recommend enabling it.
iOS
To enable card scanning support for iOS, set the NSCameraUsageDescription (Privacy - Camera Usage Description) in the Info. of your application, and provide a reason for accessing the camera (for example, “To scan cards”).
Optional Android
To enable card scanning support, request production access to the Google Pay API from the Google Pay and Wallet Console.
- If you’ve enabled Google Pay, the card scanning feature is automatically available in our UI on eligible devices. To learn more about eligible devices, see the Google Pay API constraints
- Important: The card scanning feature only appears in builds signed with the same signing key registered in the Google Pay & Wallet Console. Test or debug builds using different signing keys (for example, builds distributed through Firebase App Tester) won’t show the Scan card option. To test card scanning in pre-release builds, you must either:
- Sign your test builds with your production signing key
- Add your test signing key fingerprint to the Google Pay and Wallet Console
OptionalEnable Link
Enable Link in your Payment Method settings to allow your customers to securely save and reuse their payment information using Link’s one-click express checkout button.
Pass your customer’s email address to the Mobile Payment Element
Link authenticates a customer using their email address. Stripe recommends prefilling as much information as possible to streamline the checkout process.
To prefill the customer’s name, email address, and phone number, supply defaultBillingDetails with your customer information to initPaymentSheet.
await initPaymentSheet({ ... defaultBillingDetails: { name: 'Jenny Rosen', email: 'jenny.rosen@example.com', phone: '888-888-8888', }, });
OptionalEnable Apple Pay
Register for an Apple Merchant ID
Obtain an Apple Merchant ID by registering for a new identifier on the Apple Developer website.
Fill out the form with a description and identifier. Your description is for your own records and you can modify it in the future. Stripe recommends using the name of your app as the identifier (for example, merchant.).
Create a new Apple Pay certificate
Create a certificate for your app to encrypt payment data.
Go to the iOS Certificate Settings in the Dashboard, click Add new application, and follow the guide.
Download a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) file to get a secure certificate from Apple that allows you to use Apple Pay.
One CSR file must be used to issue exactly one certificate. If you switch your Apple Merchant ID, you must go to the iOS Certificate Settings in the Dashboard to obtain a new CSR and certificate.
Integrate with Xcode
Add the Apple Pay capability to your app. In Xcode, open your project settings, click the Signing & Capabilities tab, and add the Apple Pay capability. You might be prompted to log in to your developer account at this point. Select the merchant ID you created earlier, and your app is ready to accept Apple Pay.
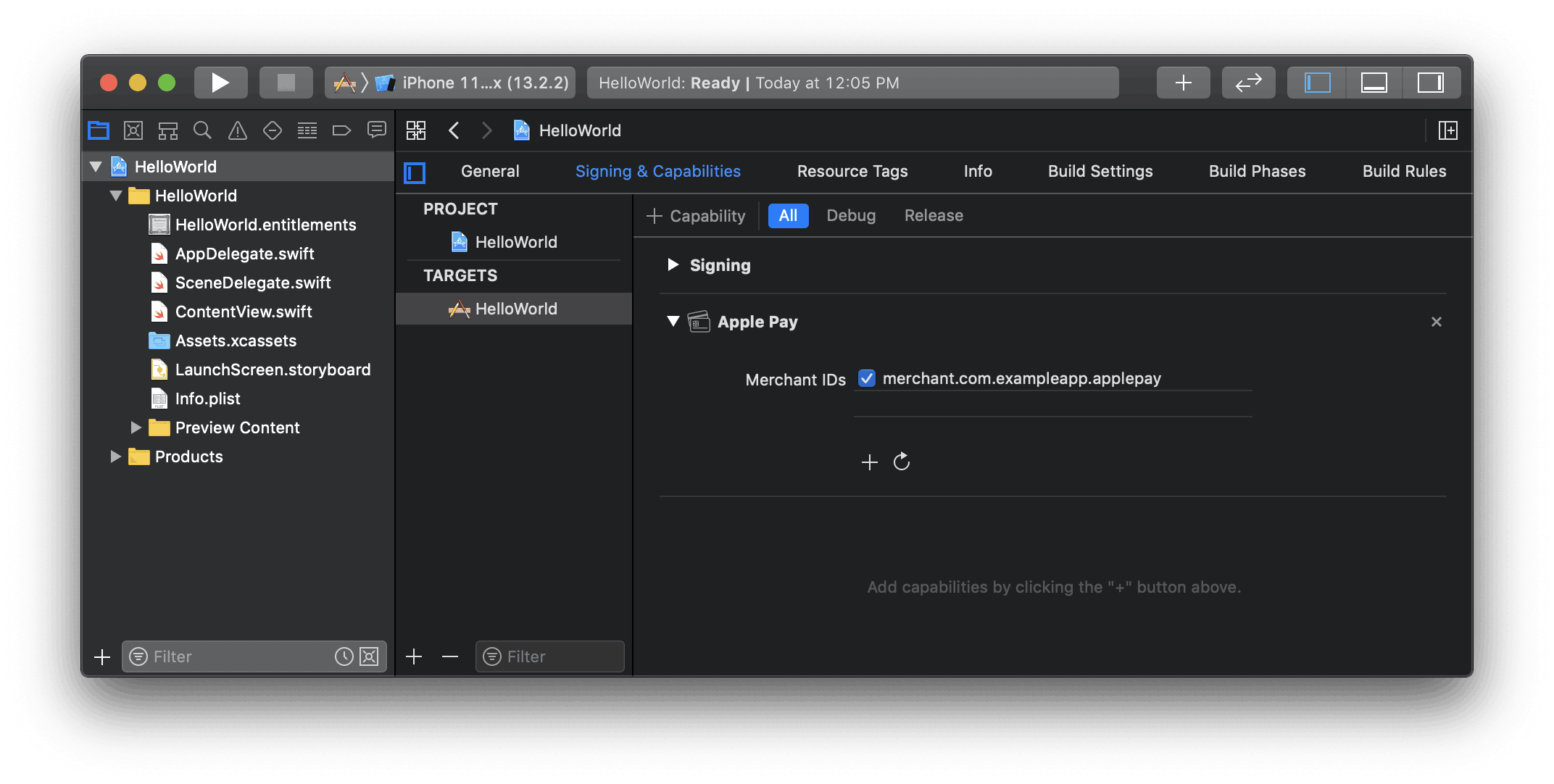
Enable the Apple Pay capability in Xcode
Add Apple Pay
Order tracking
To add order tracking information in iOS 16 or later, configure a setOrderTracking callback function. Stripe calls your implementation after the payment is complete, but before iOS dismisses the Apple Pay sheet.
In your implementation of setOrderTracking callback function, fetch the order details from your server for the completed order, and pass the details to the provided completion function.
To learn more about order tracking, see Apple’s Wallet Orders documentation.
await initPaymentSheet({ // ... applePay: { // ... setOrderTracking: async complete => { const apiEndpoint = Platform.OS === 'ios' ? 'http://localhost:4242' : 'http://10.0.2.2:4567'; const response = await fetch( `${apiEndpoint}/retrieve-order?orderId=${orderId}`, { method: 'GET', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', }, }, ); if (response.status === 200) { const orderDetails = await response.json(); // orderDetails should include orderIdentifier, orderTypeIdentifier, // authenticationToken and webServiceUrl complete(orderDetails); } }, }, });
OptionalEnable Google Pay
Set up your integration
To use Google Pay, first enable the Google Pay API by adding the following to the <application> tag of your AndroidManifest.xml:
<application> ... <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.wallet.api.enabled" android:value="true" /> </application>
For more details, see Google Pay’s Set up Google Pay API for Android.
Add Google Pay
When you initialise PaymentSheet, set merchantCountryCode to the country code of your business and set googlePay to true.
You can also use the test environment by passing the testEnv parameter. You can only test Google Pay on a physical Android device. Follow the React Native docs to test your application on a physical device.
const { error, paymentOption } = await initPaymentSheet({ // ... googlePay: { merchantCountryCode: 'US', testEnv: true, // use test environment }, });
OptionalCustomize the sheetClient-side
All customization is configured using initPaymentSheet.
Appearance
Customise colours, fonts, and so on to match the look and feel of your app by using the appearance API.
Merchant display name
Specify a customer-facing business name by setting merchantDisplayName. By default, this is your app’s name.
await initPaymentSheet({ // ... merchantDisplayName: 'Example Inc.', });
Dark mode
By default, PaymentSheet automatically adapts to the user’s system-wide appearance settings (light and dark mode). You can change this by setting the style property to alwaysLight or alwaysDark mode on iOS.
await initPaymentSheet({ // ... style: 'alwaysDark', });
On Android, set light or dark mode on your app:
// force dark AppCompatDelegate.setDefaultNightMode(AppCompatDelegate.MODE_NIGHT_YES) // force light AppCompatDelegate.setDefaultNightMode(AppCompatDelegate.MODE_NIGHT_NO)
Default billing details
To set default values for billing details collected in the PaymentSheet, configure the defaultBillingDetails property. The PaymentSheet pre-populates its fields with the values that you provide.
await initPaymentSheet({ // ... defaultBillingDetails: { email: 'foo@bar.com', address: { country: 'US', }, }, });
Collect billing details
Use billingDetailsCollectionConfiguration to specify how you want to collect billing details in the PaymentSheet.
You can collect your customer’s name, email, phone number, and address.
If you don’t intend to collect the values that the payment method requires, you must do the following:
- Attach the values that aren’t collected by
PaymentSheetto thedefaultBillingDetailsproperty. - Set
billingDetailsCollectionConfiguration.toattachDefaultsToPaymentMethod true.
await initPaymentSheet({ // ... defaultBillingDetails: { email: 'foo@bar.com', } billingDetailsCollectionConfiguration: { name: PaymentSheet.CollectionMode.ALWAYS, email: PaymentSheet.CollectionMode.NEVER, address: PaymentSheet.AddressCollectionMode.FULL, attachDefaultsToPaymentMethod: true }, });
Note
Consult with your legal counsel regarding laws that apply to collecting information. Only collect phone numbers if you need them for the transaction.
OptionalHandle user logout
PaymentSheet stores some information locally to remember whether a user has used Link within an app. To clear the internal state of PaymentSheet, call the resetPaymentSheetCustomer() method when your user logs out.
export default function CheckoutScreen() { // continued from above const { initPaymentSheet, presentPaymentSheet, resetPaymentSheetCustomer } = useStripe(); const logout = async () => { await resetPaymentSheetCustomer(); }; return ( <Screen> <Button title="Checkout" onPress={openPaymentSheet} /> <Button title="Checkout" onPress={logout} /> </Screen> ); }
OptionalComplete payment in your UI
You can present Payment Sheet to only collect payment method details and then later call a confirm method to complete payment in your app’s UI. This is useful if you have a custom buy button or require additional steps after payment details are collected.

Note
A sample integration is available on our GitHub.
- First, call
initPaymentSheetand passcustomFlow: true.initPaymentSheetresolves with an initial payment option containing an image and label representing the customer’s payment method. Update your UI with these details.
const { initPaymentSheet, presentPaymentSheet, confirmPaymentSheetPayment, } = useStripe() const { error, paymentOption } = await initPaymentSheet({ customerId: customer, customerEphemeralKeySecret: ephemeralKey, paymentIntentClientSecret: paymentIntent, customFlow: true, merchantDisplayName: 'Example Inc.', }); // Update your UI with paymentOption
- Use
presentPaymentSheetto collect payment details. When the customer finishes, the sheet dismisses itself and resolves the promise. Update your UI with the selected payment method details.
const { error, paymentOption } = await presentPaymentSheet();
- Use
confirmPaymentSheetPaymentto confirm the payment. This resolves with the result of the payment.
const { error } = await confirmPaymentSheetPayment(); if (error) { Alert.alert(`Error code: ${error.code}`, error.message); } else { Alert.alert( 'Success', 'Your order is confirmed!' ); }
Setting allowsDelayedPaymentMethods to true allows delayed notification payment methods like US bank accounts. For these payment methods, the final payment status isn’t known when the PaymentSheet completes, and instead succeeds or fails later. If you support these types of payment methods, inform the customer their order is confirmed and only fulfil their order (for example, ship their product) when the payment is successful.